Verify De Morgan S Law Using Venn Diagram

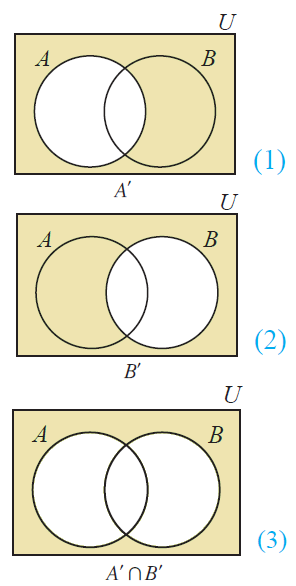
Use venn diagrams to verify demorgan s second law.
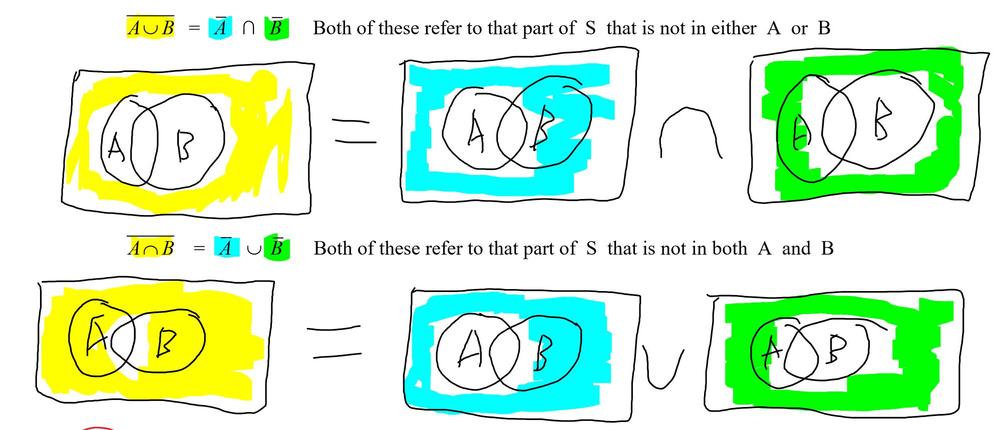
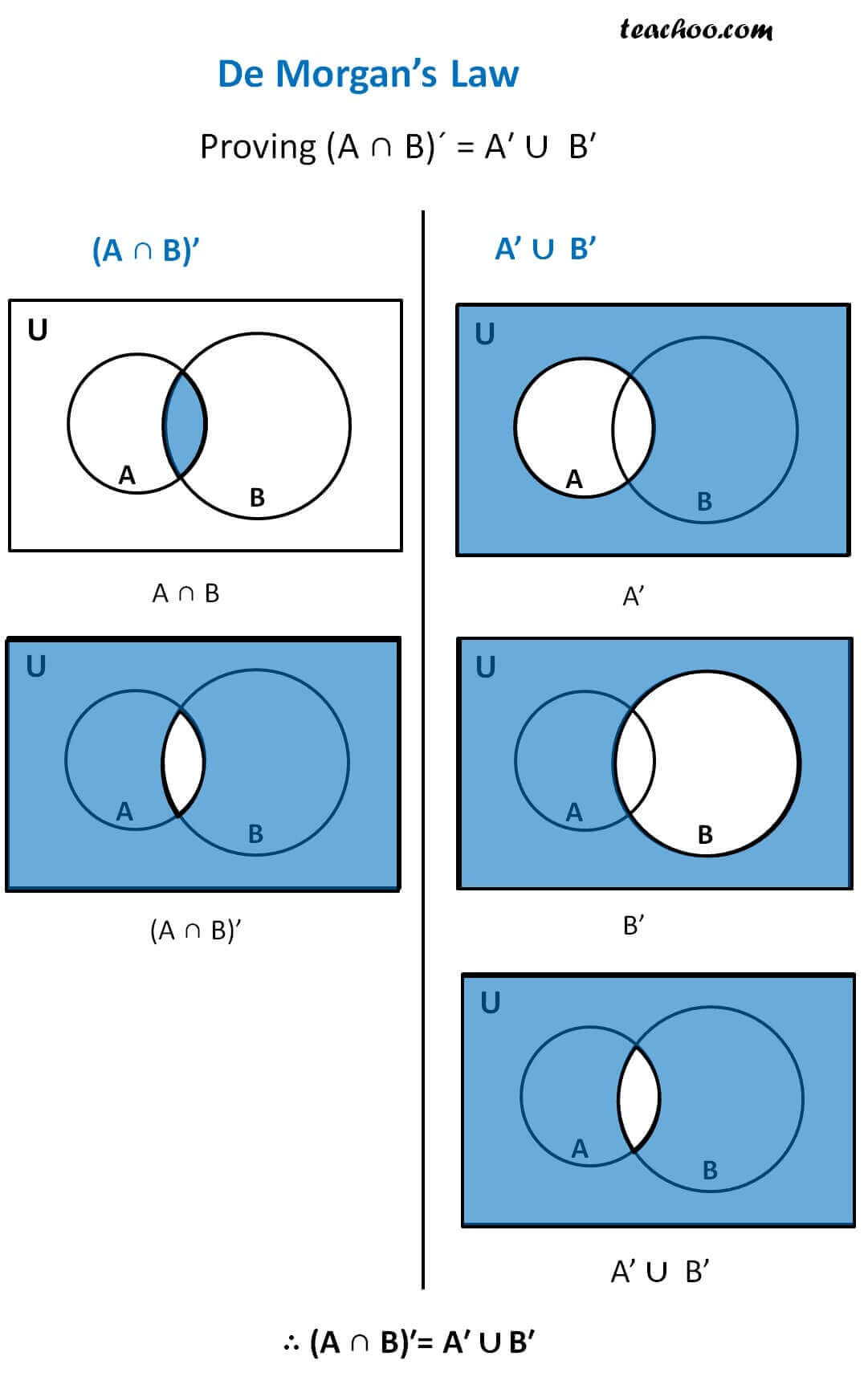
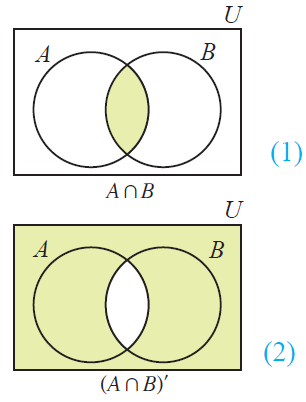
Verify de morgan s law using venn diagram. Augustus de morgan 1806 1871 was born in madurai tamilnadu india. Consider set a and set b. Let us take the first part of this equation and represent it in a venn diagram. Let s validate to morgan s laws using venn diagrams.
This article explains the de morgan laws with the help of venn diagrams. Set q is made up of elements 2. Click here to get an answer to your question use venn diagrams to verify de morgan s law of complementation a b a b 11th. Asked on october 15 2019 by sumitha harjai.
Set p is made up of elements a million and a pair of. Introduction to probability and its applications 3rd edition edit edition. P q p q. Now let us look at the venn diagram proof of de morgan s law for complementation.
Problem 16e from chapter 2. Now to the second part of the law which is the same as. Use venn diagrams to verify. Applied to set theory de morgan s law states let s dig deeper into this law.
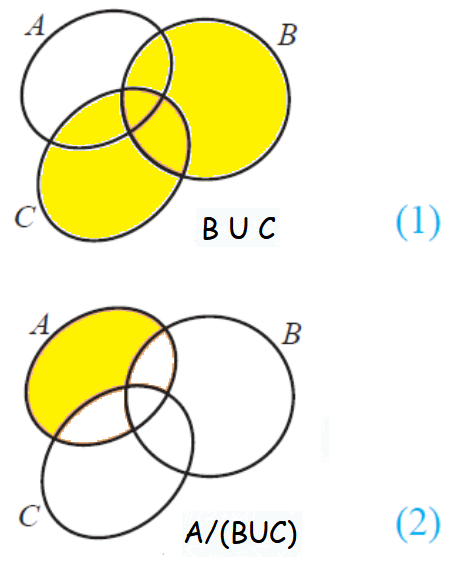
Let s draw this out in venn diagrams to really get a sense of what this represents first listed on the sample space and now we ll draw two sets a. That represent 2 instruments in a venn diagram. First let s state to morgan s first law. From the above venn diagrams 2 and 5 it is clear that a b n c a b u a c hence de morgan s law for set difference is verified.
De morgan s father a british national was in the service of east india company india. P with playstation for spacing and sq. He had his education at trinity college cambridge england. A n b a u b.
I had to fill sq. Use venn diagrams to verify de morgan s law for set difference a. Using venn diagrams to verify set identities including de morgan s law the probability identity of either of two events happens or both happen by definition the sample space contains all possible outcomes of an experiment. Learn the explanation to de morgan s laws.
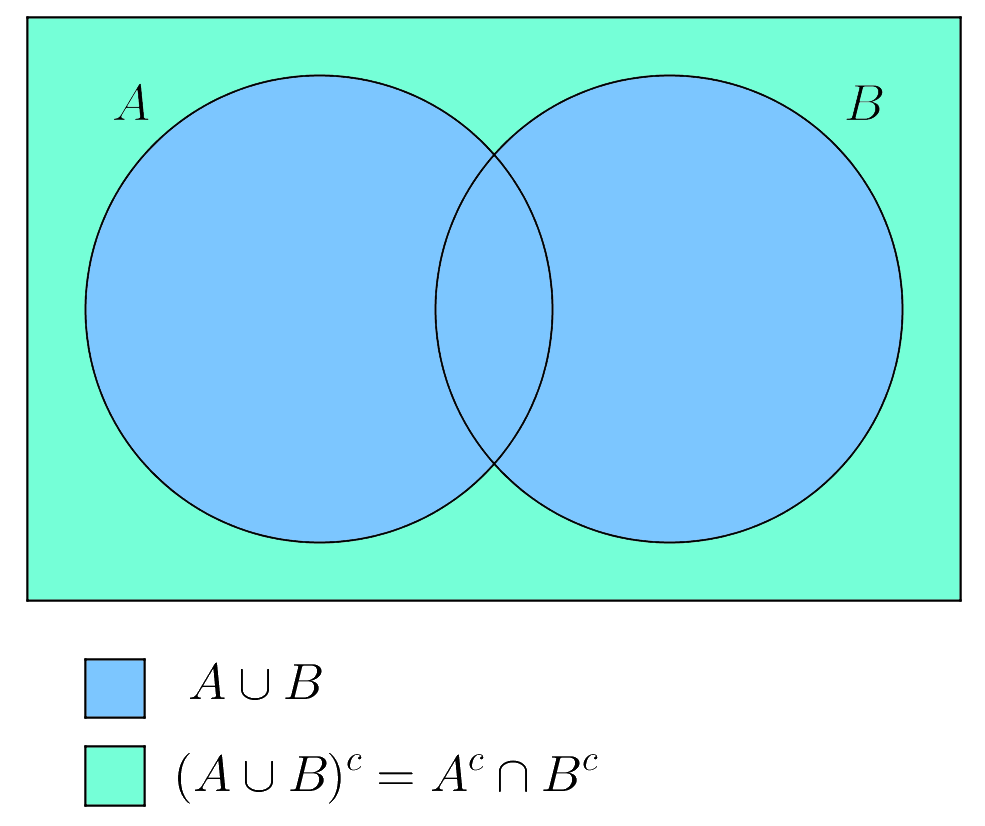
His family moved to england when he was seven months old. De morgan s laws in set theory states that complement of the union of two sets is equal to the intersection of co.

.png)